Semantic SEO: A Comprehensive Guide for 2026 (Tips+Tools+Examples)
Old SEO tricks aren’t cutting it anymore. Google now understands not just the words you type but the meaning behind them. That’s why stuffing pages with keywords won’t get you far.
If you want to rank in 2026, you need a strategy that matches how search engines think. That’s where Semantic SEO comes in. It’s about building content that answers every possible question your audience might have, while speaking the same “language” Google’s AI understands.
In this guide, you’ll learn how Semantic SEO works, why it’s the future of search, and exactly how to use it to boost your rankings.
We’ll break it down into practical steps, real examples, and the best tools to get you started.
Quick Summary
Semantic SEO focuses on topics, context, and user intent instead of just exact-match keywords. By organizing content into topic clusters, using related terms and entities, and adding schema markup, you help Google understand your site’s meaning, not just its words.
This boosts rankings for a wider range of searches, improves relevance, and future-proofs your SEO in the age of AI-driven search.
What is Semantic SEO and How Does It Work
In the past, SEO was mostly about using as many keywords as possible. But now, with semantic SEO, it's more about understanding what people are really looking for.
By knowing the connection between words and what people want, you can make content that's both good for search engines and interesting for your visitors.
Semantic SEO is the idea of creating content for a topic instead of a keyword.
It means you should consider the search intent and provide the user with all the information he is looking for by creating quality and in-depth content.
A few years back, people used to crack top search engine rankings by repeating the same keywords multiple times in a single content. Like, if you created a blog on Semantic SEO by placing Semantic SEO keywords several times in your blog, you would get top ranking that time.

Those days are gone. Now you have to create content for multiple keywords and you have to focus on the topic.
So, a piece of content that is properly optimized for Semantic SEO will not only answer the question that a user has now but it will also answer all the related questions he may have after reading the content.
For example, if you google “Semantic SEO”, you wouldn't be happy to open an article that simply gives you the answer to what Semantic SEO is. You would also want to know how Semantic SEO works, how you can optimize your site for Semantic SEO, and so on.

A good Semantic SEO-optimized article would cover all content angles behind a search query.
Why is Semantic SEO Important for Your Business?
Semantic SEO allows the creation of content with a bigger purpose. The pages that use this SEO strategy usually have higher rankings on the search and more in-depth content for users.
Google wants to provide users with the most valuable and helpful content, and following Semantic SEO only increases the chance of your content being recognized as one. Taking into consideration Google’s E-E-A-T principles also helps to create high-quality content.
Let's check some crucial benefits of practicing Semantic SEO for your site-
1. Your Content Ranks Higher
The main benefit of semantic SEO is that your content will rank higher in the search results because it will better reflect the topic model that the search engine has built for that keyword.
2. You Rank for More Keywords
Another major benefit of semantic SEO is that you end up ranking for more keywords. When you write content around an entire topic, you tend to use more of the semantically related keywords associated with that topic.
And that means that your content piece is going to show up in many more searches than if you focus on a single keyword.
3. You Send Quality Signals to Google
Also, writing topic-focused content will send quality signals to Google: your website will be seen as having topical authority for the topics that you write about. That means that when you write new content on a related topic, you’ll find it easier to rank in the search results.
4. Your Content Shows up in PAA
‘People Also Ask’ is another benefit of using semantic SEO. When you cover every aspect of a topic, your content is more likely to be chosen as a source for answering ‘People Also Ask’ features.
According to Ahrefs 43% of all searches now show a ‘People Also Ask’ box. So this is a strategy that can dramatically increase your traffic.
5. Your Visitors Stay on Your Website Longer
Content that covers every aspect of a topic keeps visitors on your page for longer. That's a user experience signal that will help your content rank higher. Also, it helps to reduce the bounce rate of your site.
How Semantic SEO Came into Existence (3 Google Search Algorithm Updates Explained)
During the early days of searching, some people started stuffing their websites with relevant keywords. This helped them achieve higher rankings in SERPs even if they did not provide the best solution. This set Google on the path to explore ways to make its algorithm understand human language.
This was how the Google search result page looked before introducing Semantic SEO.
To meet the highest quality standards, Google considers a variety of factors that ultimately influence what you see in search results. For this, Google devised a complicated system based on several algorithms that crawl, rate, and deliver the most relevant pages for a given query.
As a result, Semantic SEO came into the scenario.
Google uses artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to provide the best SERP results and improve the UX. They are also important to maintain a successful semantic search. Therefore, Google constantly releases updates to its algorithms to make Semantic SEO more and more mature.
Let's check some of the most crucial Google Semantic SEO updates-
I. Hummingbird
Hummingbird is a Google update that rolled out in 2013 and is arguably the beginning of the Semantic Search regime as we know it today. It uses NLP (Natural Language Processing) to make sure that webpages matching the meaning do well, rather than pages matching just some words.
Therefore, this implies that pages that better match the searcher setting and purpose will rank better compared to pages that recurrent setting fewer keywords relentlessly.
If you search “potato wedges“, the SERP does contain standard organic results and links to suitable websites, but it also contains a rich set of knowledge graph data, including an answer box with a recipe, a right-hand knowledge panel featuring nutritional facts about this food, and suggestions for related search subjects.
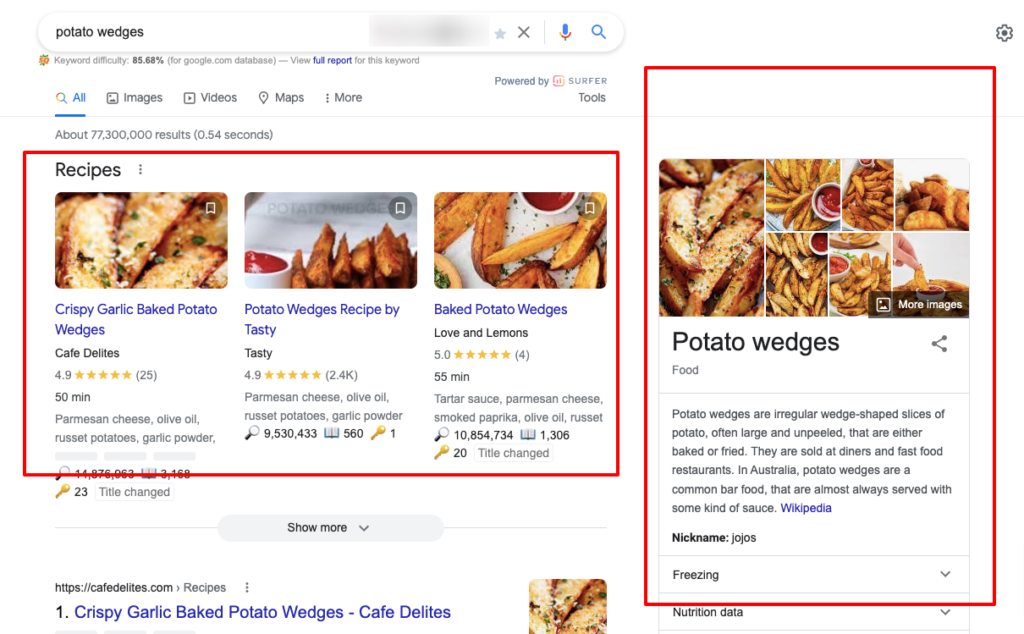
This was the output of the Google Hummingbird update and the start of the Semantic SEO era.
II. RankBrain
Google launched RankBrain in 2015. It is a machine learning system that's both a smart query analysis AI and a ranking factor. RankBrain, similar to Hummingbird, tries to comprehend the searchers' goal behind questions. The basic distinction between them is RankBrain's AI part.
RankBrain continually picks up, investigates the best-performing query items, and searches for similitudes between the pages that clients discover important.
III. BERT
Google introduced BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) in 2019. This spotlights on additional getting plan and discussion search setting. BERT permits clients to find and effectively discover significant and precise data easily.
It uses NLP (Natural Language Processing) technology to even better understand search queries, interpret text, and identify relationships between words, phrases, etc.
All of these updates are made to optimize the computer’s understanding of the context behind search queries. It’s an in-depth machine analysis of words and intentions.
Semantic SEO vs Traditional SEO: Major Differences You Should Know

Traditional SEO is the process of optimizing your site or content for search engines. You'll prioritize keyword-based content rather than topic-based content in terms of traditional SEO. That means your focus is on preparing your content for search engines, not serving users' intent.
Regardless to say, Semantic SEO removes this gap between your content and your user's intent. It focuses on creating content to serve users' intent.
Semantic SEO is the bridge between your content and users' intent. This is the biggest difference between Traditional SEO and Semantic SEO.
However, this is not like keyword research is invalid for Semantic SEO. It's also a vital part of Semantic SEO.
The difference is Semantic SEO suggests publishing content for different keywords whereas traditional SEO is likely to publish content based on a single keyword.
Also, Semantic SEO is here to increase user experience, as it focuses on creating long content with every possible information for a specific topic. That means users will get all the information in one place rather than finding it from different blogs.
Check this Semantic SEO vs Traditional SEO comparison table to get a more clear idea.
| Semantic SEO | Traditional SEO | |
|---|---|---|
| Content Optimization Type | Topic-based | Keyword-based |
| Optimized to Meet | User intent | Search engine needs |
| User Experience | Better user experience | Comparatively lower user experience |
| Bounce Rate | Improves bounce rate | Not committed to improving bounce rate |
7 Semantic SEO Best Practices to Get Better Rankings
Here we will discuss the proven tips of Semantic SEO to get the best result in SERP for your site. At first, let's take a quick look at the list.
- Try to Understand User Intent
- Focus on Creating Content Outline
- Create Detailed Content
- Optimize for Multiple Keywords (Semantic Keywords)
- Answer People Also Ask Questions
- Follow Topic Clustering
- Add Structured Data
Now we are going to learn each of the above-mentioned points. So, let's get started!
1. Try to Understand User Intent

The most important thing you must do to optimize your content for Semantic SEO is to understand the intent behind the search query. Search engines like Google want to offer a user journey that completely addresses the intent behind the query.
They don't want to offer randomly generated fragments of content. This means that you need to map out what it is that the searcher ultimately wants to do.
Let's assume a searcher searches “how to use WordPress”. But we can also anticipate some other information he will need:
- What are the benefits of using WordPress?
- Is WordPress better than other CMSs?
- Best plugins and themes to use with WordPress?
- How much it will cost to use WordPress?
- How to design a website with WordPress?
- Best domain and hosting for WordPress
If you can provide all of that information in your content, that provides a better user experience for the searcher. Instead of hopping around from one article to another, they can get all the information they need in one place.
That piece of content is going to rank higher in search engines because it offers a better user experience than articles that just address one aspect of the topic.
2. Focus on Creating Content Outlines
Another key strategy in semantic SEO is to create an outline for your article. Your content piece needs to be carefully structured around the subtopics within your main topic. Having a well-structured outline is how you ensure that you are covering the topic comprehensively.
Your outline should be divided into main sections (H2 headings) and subsections (H3 headings). Depending on how detailed the material is, you may also need sections within your subsections (H4 headings).
When researching your content, treat each main section (i.e. each H2 heading) as its own article. Don't give us that look!
Let's explain!
Suppose, the topic of your article is “Barbecue Chicken Pizza“. Your main sections (H2 headings) might be ‘Barbecue chicken pizza recipe’, ‘Best restaurant to get barbecue pizza’, ‘Health concern with Pizza’, and ‘Best time to have Pizza’.
Research each of those topics as if it were an article on its own. When you take that approach it ensures that your piece of content will have topical authority and will be more authoritative than other articles on the same topic.
3. Create Detailed Content
Detailed content means in-depth content. This refers to how much detail your content covers for a given topic. Although content length is not an official ranking factor, longer content is more likely to display stronger semantic signals.
But simply relying on keyword stuffing or repetition to improve content length is not going to prove effective. Then how should you plan for detailed content?
Well, there is an easy way to do that. You can search for your topic in the search engines and go through the top results. Then you'll get the idea of how much information you should cover to answer all the possible questions of your readers.
Another smart way to put detailed information on a given topic is to use Answer The Public. How? Suppose, your topic is “Semantic SEO”, go to “Answer The Public” and search for “Semantic SEO”. See the result.
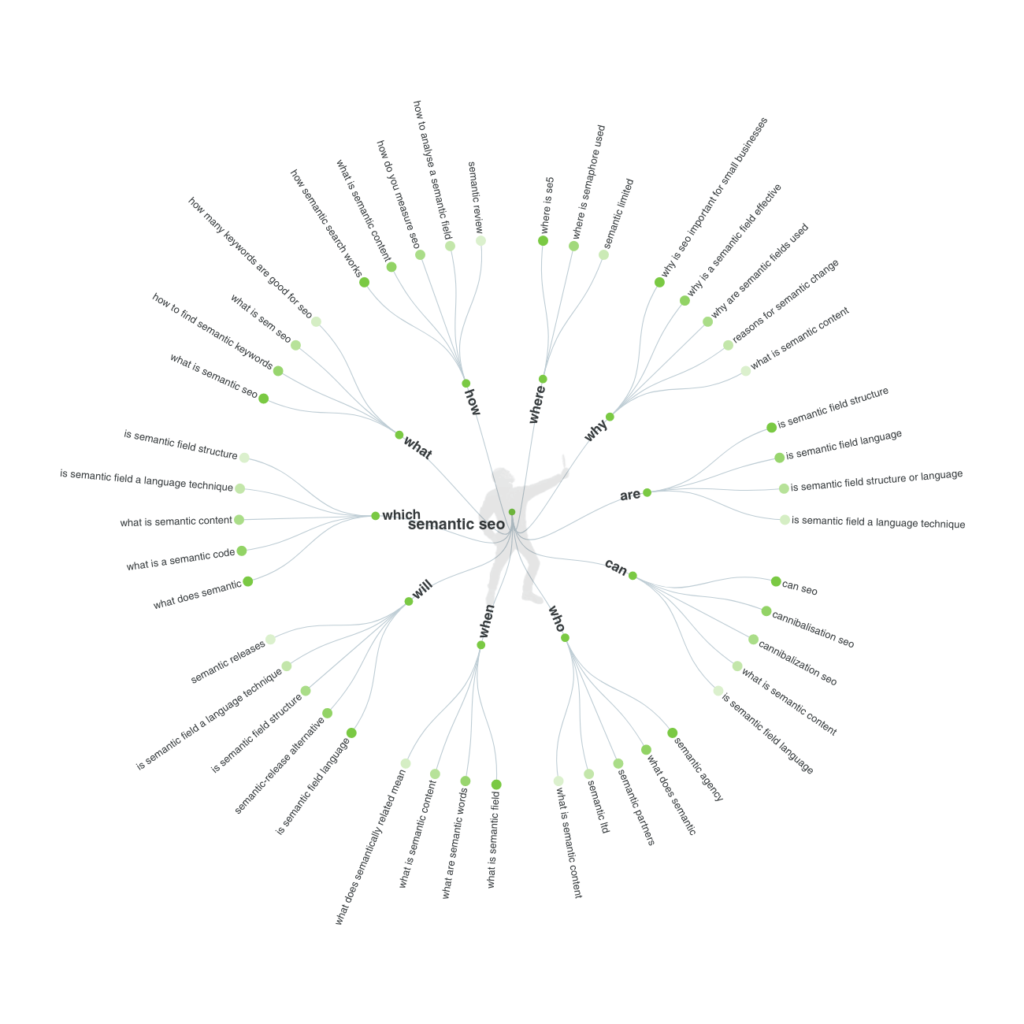
That means now you have 40+ questions related to Semantic SEO to cover in your blog. Obviously, not all the questions will be relevant to your blog, but most of the questions you can go for.
This is how you can create detailed content- that is the first point to optimize your content for Semantic SEO.
Want to check a detailed content for inspiration? Check out our in-depth blog on local SEO to learn how a pillar content should be written.
4. Optimize for Multiple Keywords (Semantic Keywords)
The main idea behind Semantic SEO is to optimize your content for multiple keywords. Keyword research is, in a nutshell, complex. Most authors just do simple keyword research on individual keywords that are relevant to their products and services.
But if you’re practicing semantic SEO, you need to go one step further by incorporating semantic keywords too.
What are semantic keywords?
They’re simply words or phrases that are related to each other by the concept. Put differently, they don’t need to share the same words, just the same topic.
This includes verbs, adjectives, related questions, phrases, subtopics, and LSI keywords. There are several tools to find out related and LSI keywords for your topic. Also, you can use Google-suggested keywords to optimize your content. Here is an example:
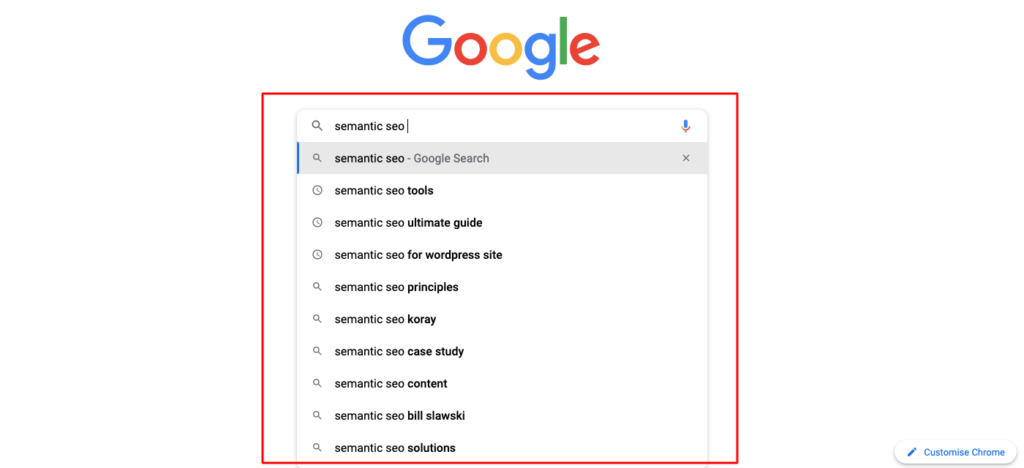
When you are writing about “importance of physical exercise for good health”, you should start with the keyword tips to be healthy. Semantically related keywords might include:
- List of foods for weight loss
- protein shake recipe
- low-carb meals, and so on.
When you enhance your keyword research and double down on content creation, you will have great success in creating relevant content. That content will also appear higher up in the search results for more relevant keyword phrases.
5. Answer People Also Ask Questions
When you search for anything on Google, you see the People Also Ask section on the first page, more precisely, after the featured snippet or zero position.
This is the list of questions that people mostly asked for. Google itself ranks these questions, so addressing these questions in your blog could be a good reason to increase the user experience of your blog. And improving user experience is one of the core ideas of Semantic SEO.
Here is an example of the “People also ask” section of Google.
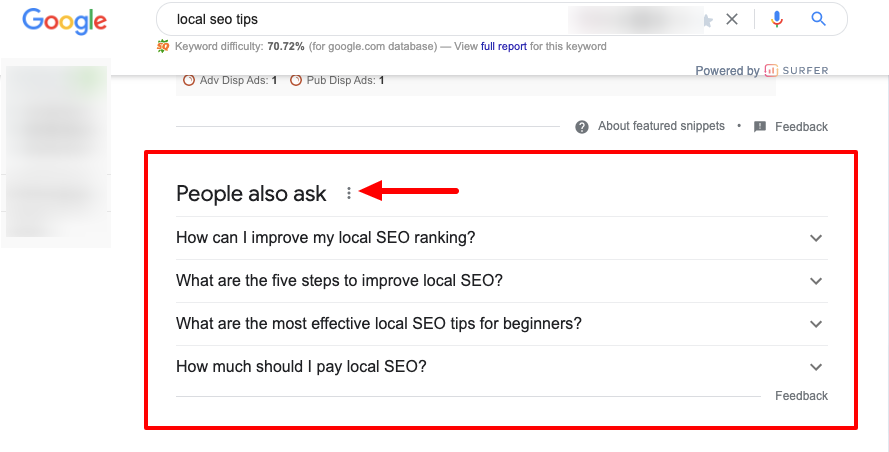
By answering those questions in your web page content, not only do you improve your semantic signals, you also give your page the opportunity to rank at the top of the SERPs.
6. Follow Topic Clustering

A topic cluster is a group of pages that revolves around a central topic. It uses a pillar page as the main hub with the cluster pages all linking to and from the pillar page.
That means you will publish content on a given topic. Then publish a few more blogs related to that given topic.
Suppose, you want to create content on “How to promote a plugin“. The pillar post would briefly mention the subtopics within plugin promotion, such as:
- Best ways to develop a WordPress plugin
- Top marketplaces to promote your plugin
- Understand pricing psychology
- Digital marketing ways to promote your plugin
- Inbound marketing to promote your plugin
Your article on “plugin promotion” would link out to separate pages that cover these individual topics in more detail.
Topic clusters are great for semantic SEO because they show search engines that your site has topical authority on that topic. In addition, the internal linking that results from a topic cluster sends an important topical relevance signal to search engines.
7. Add Structured Data
To help Google better understand your content, use structured data (Schema). It's a format for classifying the content on a page. Structured data is a language that explains to search engines what content to display in an attractive way.
With the help of structured data, what your article is about, subject, description, image, video, type, ratings, reading minutes, and so on can be conveyed easily. Structured data makes your content easily understandable to both readers and search engines.
Check this example to understand what structured data looks like:
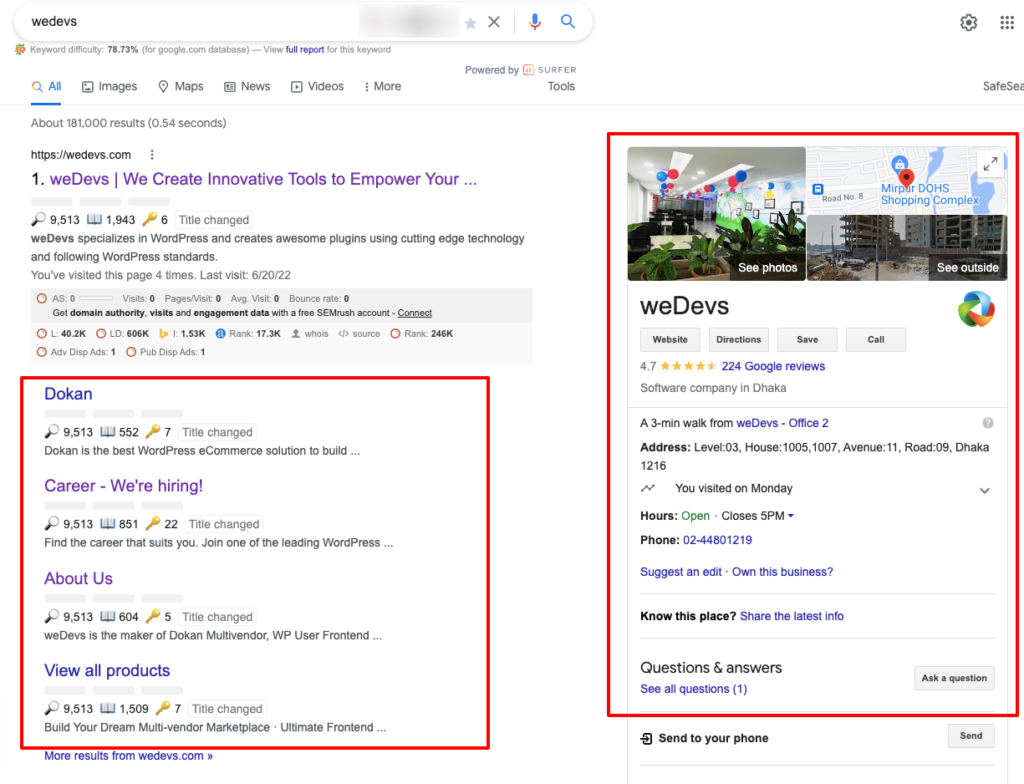
You can use Schema.org to create structured data for your content. It provides a framework that helps you describe what your content means and how it is related to other things on your website. At a minimum, the schema will help search engines more accurately index your content.
Assuming your content is also good, implementing structured data may help some of your pages rank higher in organic results.
Note: There are multiple free plugins in WordPress.org to create and use structured data for your blog.
Bonus Tip: Practice Smart Internal Linking
Internal linking is the process of linking pages on the same website. When you follow topic clustering, linking pages internally is a must for you. Apart from topic clustering, you should link internally when you create a post on your site.
A well-considered internal link structure will help your content show up at the right place in search. By linking pages together, you not only help readers navigate your site but also help Google crawl it easily and discover new pages.
For example, if your theme landing page appears higher in search results. Giving links from this page to another page (e.g., theme demo page) increases the chance of getting a higher position for this page as well.
In other words, the smarter your content is linked to each other, the better effect it will have on Google and its users.
3 Popular and Free Tools for Semantic SEO

No free tool for Semantic SEO is enough capable to take care of your site's Semantic SEO single-handedly. Then again, you can use the following tools to get some part of Semantic SEO's task done.
i) Google Autocomplete
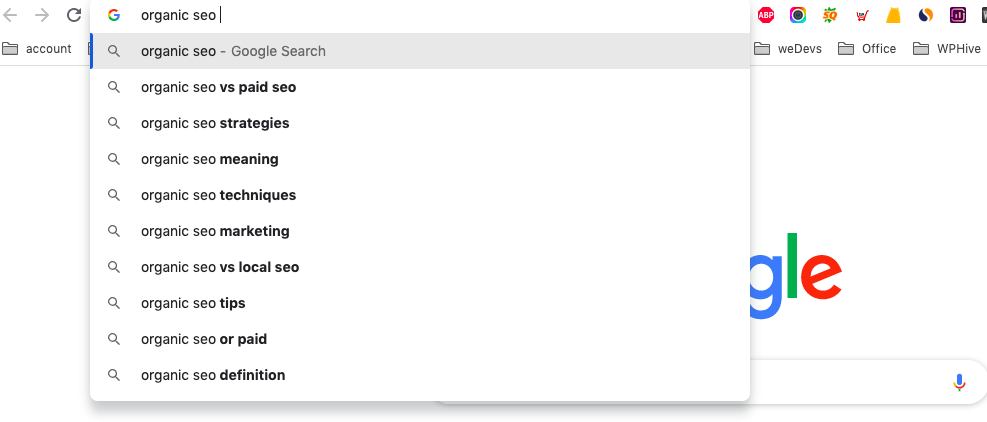
You already use Google autocomplete for your blog, right? You can use this suggestion to find Semantic keywords for your content. Go to Google, type a keyword on the search bar, enter space, and get the suggestions.
ii) Google Related Searches
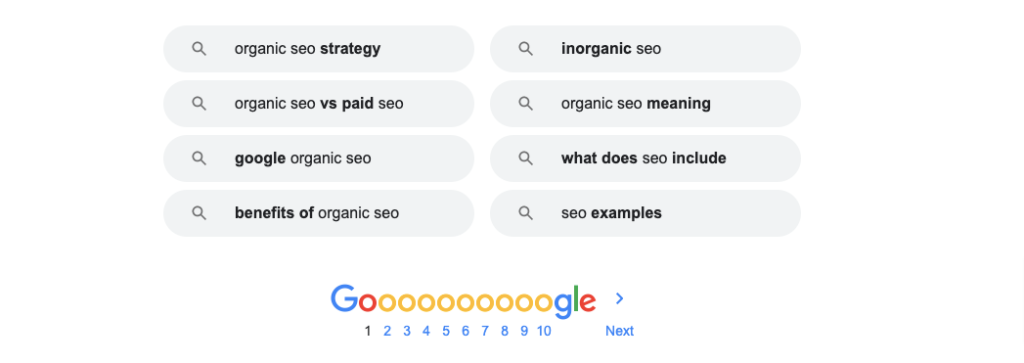
You can find LSI keywords for your main keyword from the Google Related Searches. Go to Google, type your main keyword, and scroll down to the result page, there you'll find a related keywords list.
iii) Answer The Public
We have already talked about Answer The Public. This is one of the best places to find semantic keywords for your main keyword.
Go to the site, type your keyword in the search box, then you'll get the list.
Inspirational Case Studies of Semantic SEO
Case Study 01
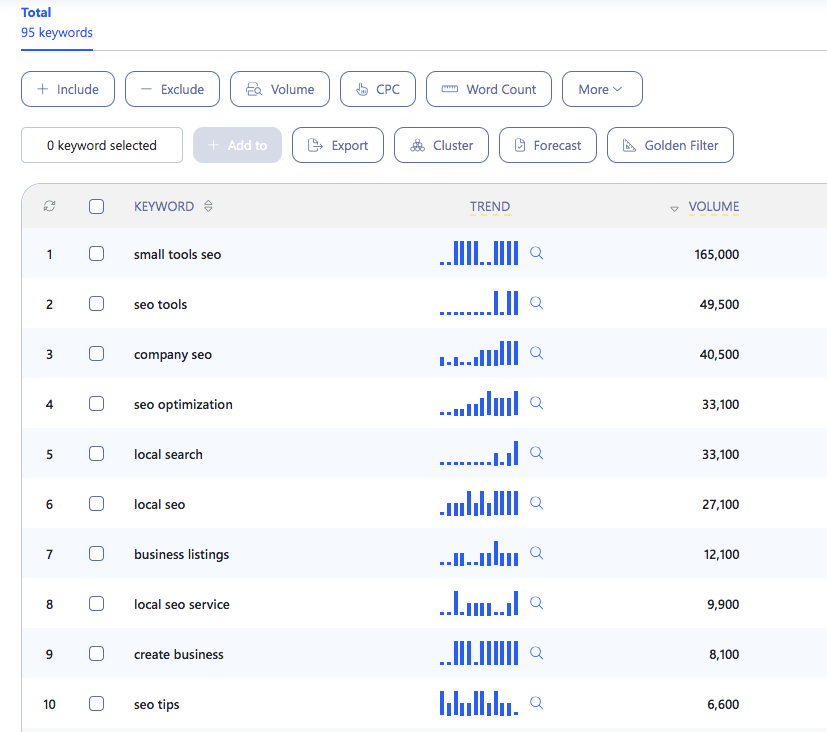
We have been practicing Semantic SEO over the years. We have planned, created, and written a blog “Local SEO Tips” following the semantic SEO strategies. As a result, we got the top position on SERP.
If you search “Local SEO” on Google, you'll get this blog on the first page. The volume of the keyword is more than 6000.
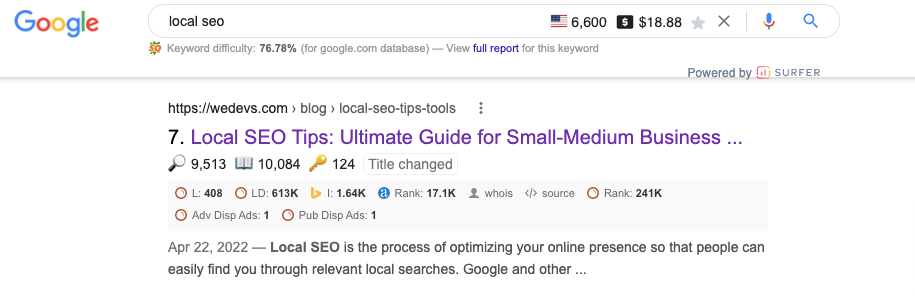
We have created a 10,000-word long blog on this topic. Here is the content outline of that blog.

This blog covers everything about Local SEO. As a result, multiple keywords from this blog have been picked by Google.
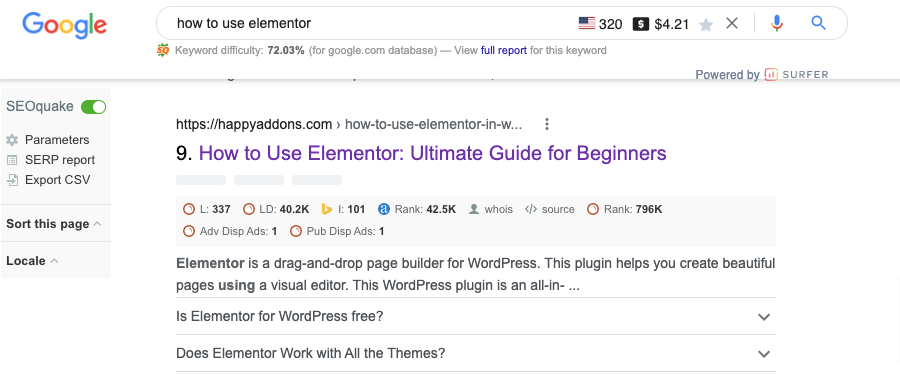
Case Study 02
Here is another example of Semantic SEO. We have created a blog on “How to use Elementor“. The search volume is more than 300. And we got the ranking on the first page.
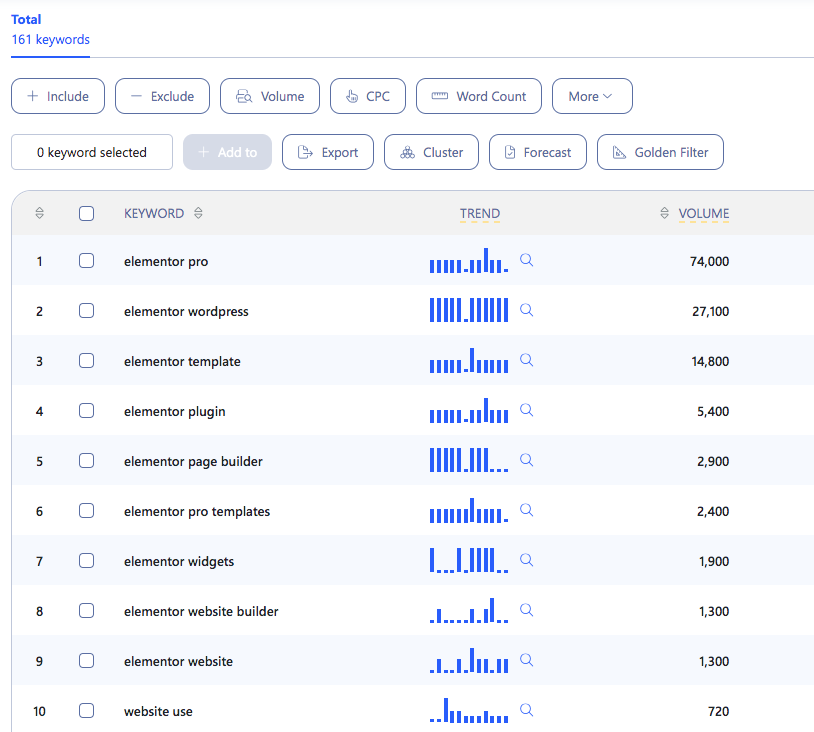
This blog is 6000 words long. Here is the outline of that content.

This blog covers everything about Elementor. As a result, Google has picked more than 160 keywords from this blog.
So, we are highly encouraging you to follow Semantic SEO while creating content for your site.
Semantic SEO – FAQs
I. What is Semantic search SEO?
Semantic search SEO is the process of how a search engine generates the most accurate search result by understanding searcher intent and keywords.
II. What is semantic SEO structure?
Semantic SEO structure is a technique that improves website traffic by providing meaningful metadata and semantically relevant content that can accurately answer a specific search intent.
III. Is Google a semantic search?
Yes, Google follows semantic search algorithms. When you search anything on Google, with the help of Semantic SEO, Google tries to understand the searcher's intent and offers answers as per the query.
IV. Why is semantic SEO important?
Semantic SEO is important. Because it helps to;
- get a higher ranking for your content
- rank more keywords
- understand Google that you have a trustworthy site.
- rank your content in PAA (People Also Ask)
- improve bounce rate.
V. What is semantic search NLP?
In machine learning, semantic search captures the meaning from inputs of words such as sentences, paragraphs, and more. It implements NLP (Natural Language Processing) techniques to understand and process large amounts of text and speech data.
VI. What is meant by Semantic Search?
Semantic search is a technique in which a search query aims to not only find keywords but to determine the intent and contextual meaning of the words a person is using for a search.
VII. How did Google introduce Semantic SEO?
Google introduced semantic SEO through its search algorithm update. Google has released Hummingbird, RankBrain, and BERT algorithms to introduce and mature semantic SEO for us.
Semantic SEO: Your Shortcut to Long-Term Rankings
Search is evolving and fast. Google’s AI updates reward content that understands context, answers intent, and builds authority around a topic. That’s exactly what Semantic SEO delivers.
Start by mapping your topics, connecting related pages, and speaking your audience’s language, not just their keywords. Add schema, track your results, and keep refining.
The sooner you start, the sooner you’ll rank for more searches, attract higher-quality visitors, and future-proof your SEO.
Your competitors are already optimizing for meaning. It’s time you did too.
Looking for a guide to learn GEO? Check out our blog on Generative Engine Optimization to get your content cited by AI.
If you have confusion, query, or feedback regarding Semantic SEO, you're highly requested to let us know through the comment box below. We would love to co-operate with you at our earliest convenience. Take care!