A Detailed WordPress Website Security Checklist for 2026
While many website owners are fully aware of the importance of following good website security practices in order to protect sensitive information and customer data from hackers, the truth is that the vast majority of those website owners don’t actually follow a good security plan that works.
You see, website security goes way beyond simply setting secure passwords or enabling two-factor authentication to log in. Did you know that only 8% of WordPress breaches happen?
Web hackers and cybercriminals are simply becoming far more sophisticated than ever before, and the result of that is that websites and blogs across the internet are becoming increasingly vulnerable as well.
But the good news is that when it comes to website security, there are a large number of different things that you can do to beef up your defenses to stop hackers and reduce your vulnerabilities, and that’s what we’re going to talk about today by going over a series of steps and strategies you can use to greatly increase the security of your website.
Why Website Security Is Important?

Website security is crucial for various reasons, as it safeguards both the website owner and its users. Here are some key reasons why website security is important:
- Protecting User Data
- Preventing Data Breaches
- Maintaining User Trust
- Guarding Against Malware and Viruses
- Avoiding Blacklisting
- Ensuring Business Continuity
- Meeting Regulatory Requirements
- Preventing Defacement
- Enhancing SEO
- Mitigating Financial Loss.
So you can see why WordPress website security is important.
11+ Website Security Checklist to Set Up the Perfect Security Strategy
Here are some basic steps you can take to develop a website security strategy that actually works:
- Stop Brute Force Log-In Attempts
- Watch Out For SQL Injection
- Choose A Secure Hosting Platform
- Regular Malware Scanning
- Use The Latest Version of Plugins
- Install An SSL Certificate
- Website Firewall (WAF)
- Update WordPress Version Regularly
- Use Secure WP-Admin Login Credentials
- File Permission Management
- Set Up Safelist and Blocklist for the Admin Page
- Use Trusted WordPress Themes
- Remove Unused WordPress Plugins and Themes.
Let's see them in detail-
1. Stop Brute Force Log-In Attempts
One of the most common threats that website owners face each day is hackers bombarding them with brute force login attempts. Hackers use specialized software to try every possible combination of letters, numbers, and symbols until they find one that grants them access.
Fortunately, there are a few methods at your disposal to stop brute force attacks. The simplest approach is to limit users to a fixed number of login attempts within a specified time period. However, this method has the issue that a hacker can lock out vast numbers of user accounts.

An even better method is to log out an entire IP address after a sufficient number of failed login attempts. Alternatively, you can design your website to redirect the user to an “HTTP 401” error page after a specified number of login attempts.
Beyond these measures, organizations that rely on directory-based authentication often strengthen defenses with a solution like Active Directory MFA, adding an identity layer that stops brute-force and credential-stuffing attacks even if passwords are compromised.
2. Watch Out For SQL Injection
An SQL injection attack is a code injection hacking technique where a cybercriminal will attempt to insert SQL (structured query language) statements into input fields.
The reason they will be able to accomplish this is because of poor coding in your web applications that leaves them vulnerable.
To stop an SQL injection before it happens, therefore, you will need to utilize typed and parameterized database queries, which you can accomplish using a programming language such as PHP or Java, among others.

Regular vulnerability scanning and analysis can help identify weak points in your applications before attackers exploit them through SQL injection or other injection-based attacks.
3. Choose A Secure Hosting Platform
One of the most important factors to consider when choosing a web host is security.
That being said, there’s not just one security factor to consider with a web host, but rather several.
At the bare minimum, you will want to choose a web host that offers you each and every one of the following security practices, presented in alphabetical order:
- Firewalls
- DDoS Protection
- Domain Name Privacy
- Spam Filter
- Virus Protection
Out of these, one of the most important is the firewall or a piece of software that is designed to filter requests to your web server. They will then block certain requests, based on a variety of factors before they reach your web server.
DDoS Protection is also particularly important to have. A DDoS attack, or Distributed Denial of Service, is where thousands of requests are sent to your website simultaneously, which overloads the website and causes it to shut down.
DDoS protection from your web host of choice will analyze DDoS activity on your website to block certain requests while enabling legitimate traffic to get through. That being said, while most web hosting providers offer firewalls, not all offer DDoS protection services, so be careful about your selection.
4. Regular Malware Scanning
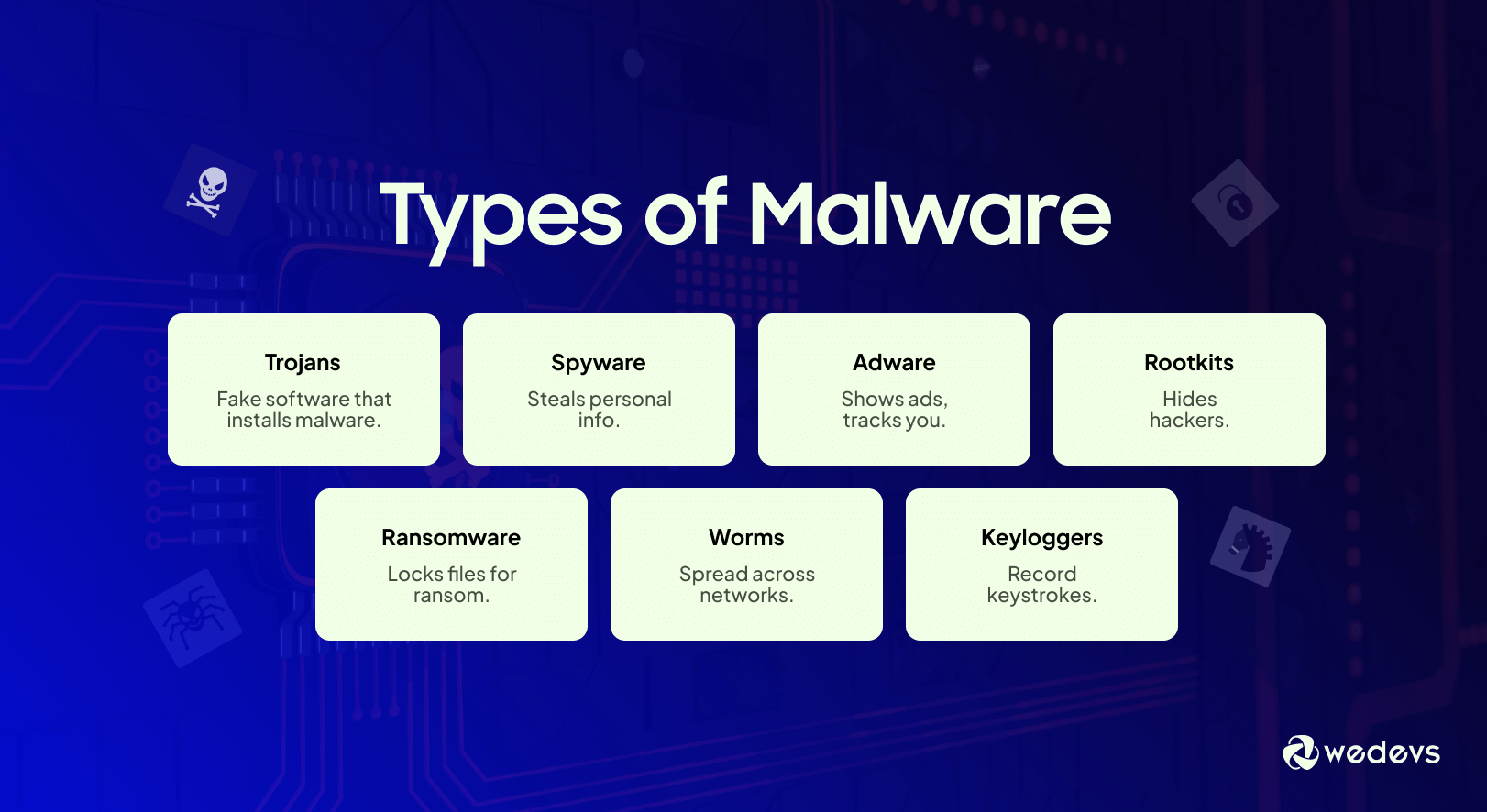
Malware is malicious software that can damage your website or steal sensitive information. Hackers often hide malware in themes, plugins, or files on your server.
Regular malware scanning helps detect suspicious files or code early, before hackers can cause serious damage. You can use plugins like Wordfence, Sucuri, or MalCare to automate the process.
These scans check for:
- Hidden backdoors
- Infected files
- Suspicious code injections
- Outdated or vulnerable scripts
Performing regular scans ensures your website stays clean and reduces the chances of blacklisting by search engines.
5. Use The Latest Version of Plugins
Updating your plugins is another critically important security strategy to follow. The longer your plugins go without receiving an update, the more likely they are to have vulnerabilities to hacking.
This is because the developers of reputable website plugins are always working hard behind the clock to patch vulnerabilities and update their plugins to keep them less exposed to attack.

That being said, over four out of every five WordPress websites don’t even have updated plugins, even though updating them is one of the easiest security procedures to do.
All that you will have to do to update your plugin is to go to the ‘Plugins’ tab (if you are running WordPress) in the dashboard, and then check to see if any of your plugins are out of date.
If any are, you simply select ‘Update Now’ and you’re all set. Simple, right? And yet it’s astonishing that the majority of WordPress website owners don’t do it.
6. Install An SSL Certificate
Last but not least, another important security step to follow will be to install an SSL certificate.
An SSL certificate is simply a data file that binds a cryptographic key to your web server’s details. This activates the HTTPS protocol, which allows secure connections between your server and the web browser.
While SSL certificates are commonly used to protect financial data and information, they are still very important to use regardless of which type of website you are running.

7. Website Firewall (WAF)
A Web Application Firewall, or WAF, acts as a shield between your website and incoming traffic. It blocks malicious requests before they reach your server.
A WAF can protect your site against:
- Brute force login attempts
- SQL injections
- Cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks
- DDoS attacks
Services like Cloudflare, Sucuri, and Wordfence offer WAF solutions specifically for WordPress. By installing a firewall, you stop most attacks at the gateway, keeping your site safe without slowing it down. Check how a web firewall can improve your website's security.
8. Update WordPress Version Regularly
Regular software updates from WordPress are crucial for enhancing performance and fortifying security, effectively safeguarding your site against cyber threats.
Updating your WordPress version stands out as one of the simplest and most effective measures to bolster security. Despite this, approximately 50% of WordPress sites persist in running older versions, leaving them more vulnerable to potential threats.
To check whether your WordPress version is up to date, log in to your WordPress admin area and navigate to Dashboard → Updates on the left menu panel. If it indicates that your version is not current, we strongly recommend updating it promptly.

It's essential to stay vigilant about future update release dates to ensure your site remains free from running outdated WordPress versions. Additionally, we advise keeping your themes and plugins up to date. Outdated themes and plugins can lead to conflicts with the newly updated WordPress core software, resulting in errors and increased susceptibility to security threats.
Follow these straightforward steps to address outdated themes and plugins:
- Navigate to your WordPress admin panel and go to Dashboard → Updates.
- Scroll down to the Plugins and Themes sections, reviewing the list of themes and plugins ready for updates. Note that you can update them collectively or individually.
- Click “Update Plugins” to ensure that your WordPress site remains secure and operates smoothly with the latest software versions.
9. Use Secure WP-Admin Login Credentials
Frequently, users make a common mistake by using easily guessable usernames like ‘admin,' ‘administrator,' or ‘test,' thereby increasing the risk that their site will fall prey to brute-force attacks. In addition, attackers often exploit these vulnerabilities to target WordPress sites that lack robust password protection.
To enhance your site's security, we strongly recommend adopting a unique, complex username and password. As an alternative, consider following these steps to establish a new WordPress administrator account featuring a distinctive username:
- From your WordPress Dashboard, navigate to Users → Add New.
- Create a new user and assign it the Administrator role. Add a password and hit the Add New User button once you’re done.

10. File Permission Management
Incorrect file permissions can give hackers access to sensitive files on your server. This can lead to file modifications, malware uploads, or even full site takeovers.
To keep your files secure:
- Set directories to
755 - Set files to
644 - Protect sensitive files like
wp-config.phpwith stricter permissions - Regularly review permissions after installing new plugins or themes
Proper file permissions ensure that only authorized users and processes can access critical parts of your website, reducing the risk of unauthorized changes. Check how to change file permission management in this post.
11. Set Up Safelist and Blocklist for the Admin Page
Securing your login page against unauthorized access and potential brute force attacks can be achieved by implementing URL lockdown. This involves utilizing a Web Application Firewall (WAF) service tailored for WordPress, such as Cloudflare or Sucuri.
When using Cloudflare, you can configure a zone lockdown rule to enhance your site's security. This rule allows you to define specific URLs that you want to lockdown, along with specifying the permitted IP range that can access these URLs. Consequently, individuals outside the designated IP range will be unable to access the specified URLs.
12. Use Trusted WordPress Themes
Nulled WordPress themes are unauthorized replicas of the original premium themes, often marketed at lower prices to entice users. However, these themes typically come with a myriad of security issues.
Frequently, providers of nulled themes turn out to be hackers who have compromised the original premium themes by embedding malicious code, including malware and spam links. Additionally, these themes may serve as potential backdoors for other exploits, posing a threat to the security of your WordPress site.

Given that nulled themes are distributed illegally, users do not receive any support from the legitimate developers. This implies that in case of any issues with your site, you'll need to troubleshoot and secure your WordPress site independently.
To mitigate the risk of being targeted by hackers, we strongly advise selecting a WordPress theme from its official repository or reputable developers. Alternatively, consider exploring third-party themes in recognized theme marketplaces like ThemeForest, where a vast selection of premium themes is available, ensuring both quality and security.
13. Remove Unused WordPress Plugins and Themes
Keeping unused plugins and themes on the site can be harmful, especially if the plugins and themes haven’t been updated. Outdated plugins and themes increase the risk of cyberattacks as hackers can use them to gain access to your site.
Follow these steps to delete an unused WordPress plugin:
- Navigate to Plugins → Installed Plugins.
- You’ll see the list of all installed plugins. Click Delete under the plugin’s name.
Note that the delete button will only be available after deactivating the plugin.
Meanwhile, here are the steps to delete an unused theme:
- From your WordPress admin dashboard, go to Appearance → Themes.
- Click on the theme you want to delete.
- A pop-up window will appear, showing the theme details. Click the Delete button in the bottom-right corner.
You can follow these to create the perfect WordPress website security checklist.
Bonus: How to Utilize WordPress Website Security Using WordPress Security Plugins
WordPress has quite a few effective security plugins to help you secure your website. These plugins will make your work easy, and you can take care of the complex tasks without any technical knowledge.
Here is how you can utilize the WordPress plugins-
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication for WP-Admin: With a plugin like WordFence Security, you can enable two-factor authentication. It will add a second layer of protection to your WordPress site.
- Back-Up WordPress Regularly: Due to WordPress or plugin/theme updates, your site can break or you can lose any data. With a WordPress plugin, you can keep a backup of your website regularly.
- Limit Login Attempts: WordPress allows unlimited attempts to log in and it opens up to outside attacks. You can use a plugin like Loginizer, to limit the login attempts.
- Change the WordPress Login Page URL: Every WordPress website shares the same default login URL: yourdomain.com/wp-admin. Relying on this default login URL can make it susceptible to hacking attempts, as it provides a predictable target for attackers. To enhance security, plugins such as WPS Hide Login and Change wp-admin Login offer the option to customize your login URL
- Monitor User Activity: What your users are doing it is also an important part of website security. There are quite a few WordPress activity log plugins to help you with that.
Guides to Help You Secure Your Website:
- How to Detect, Remove, and Protect Your WordPress Site from Malware
- Top WordPress Security Plugins
- How WordPress Firewall & Security Plugins Can Protect Your Website
Conclusion
While you would think that the majority of website owners would take the above security steps, the truth is that most of them don’t.
If you admittedly are one of those website owners who are skipping on one or more of the security strategies in this article, the good news is that you can take action to change that as early as today.
This is a guest post by Samuel Bocetta. He is a retired cybersecurity analyst, currently reporting on trends in cryptography and cybercrime.